Technical Equipment
The Institute of Mechatronic Systems has well-equipped laboratories and workshops. In the following, a variety of devices is listed.
General
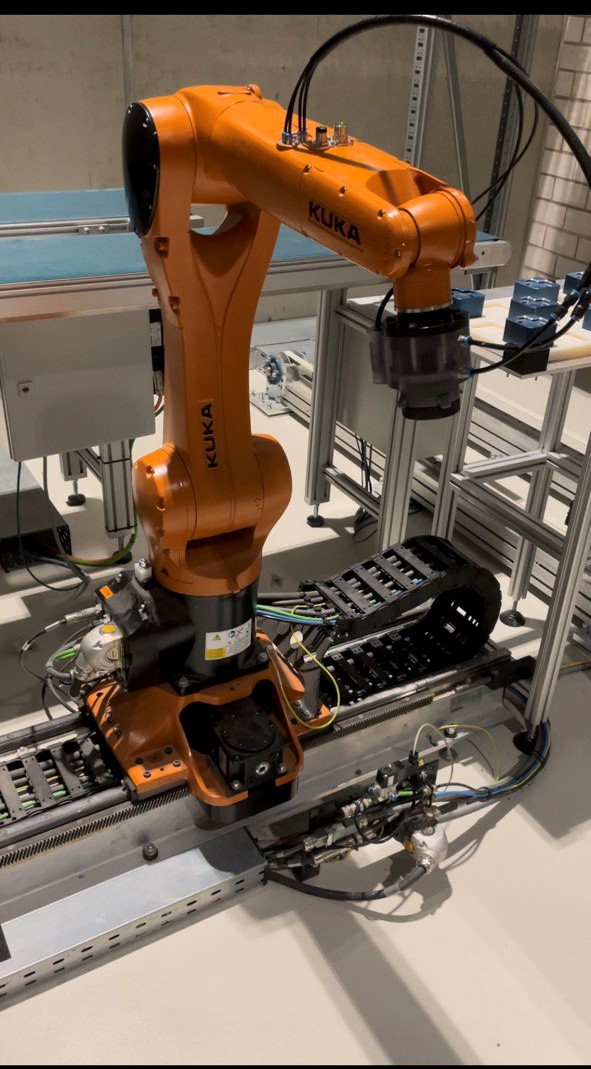
Industry 4.0 plant model: Handling process of a packaging line
The imes has a model factory with various serial and parallel kinematic robot systems at its disposal with which a fully automated handling process similar to that of a modern packaging line can be carried out. On the one hand, the system enables the application-oriented evaluation of innovative methods of robotics and control on the basis of state-of-the-art industrial drive and control technology. On the other hand, advanced methods for the analysis, monitoring and optimization of complex processes can be developed and tested in a real environment. A variable power supply concept for the electrical drive systems and close data networking of all control components with the institute's own BigData analysis platform make it possible to address a wide variety of use cases, not just from the field of industry 4.0. Training can also be carried out on the existing system.
Specification
- SCARA robot
- Delta robot with conveyor belt
- Jointed arm robot with linear guide
- Stacker crane
Robot kinematics on the model production line
-
SCARA Kinematic
The SCARA robot (Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm) is a horizontal articulated-arm robot. The SCARA features a serial kinematic structure with four segments and four degrees of freedom. As part of the IMES production line project, the robot is used for a pick-and-place task. In this task, building blocks are picked up from one of three slides and placed onto a pallet located on a conveyor belt. The picking and placing of the building blocks is performed using a pneumatic gripper with two fingers, which is mounted on the robot's last axis.
-
Delta robot with conveyor belts
As a fundamental requirement, the Delta robot is tasked with picking up workpieces (stars) from one conveyor belt and placing them onto building blocks on the other conveyor belt. The picking and placing of the stars is performed using a pneumatic suction cup mounted on the end effector.
Conveyor Belt 1:
- A pallet is ejected from the magazine.
- The pallet moves to the first light barrier.
- The SCARA robot places building blocks onto the pallet.
- The pallet continues to the second light barrier.
- The Delta robot places the stars onto the building blocks.
- The pallet moves to the third light barrier.
- The storage and retrieval machine (SRM) picks up the pallet and stores it in the shelving system.
Conveyor Belt 2:
- A star is fed onto Conveyor Belt 2 via a chute.
- The star's orientation is detected by a camera system.
- The Delta robot picks up the star within its workspace.
-
Jointed arm robot with linear guide
After the stacker crane places the pallet on the table, a KUKA robotic arm with 6 degrees of freedom and a linear axis is used to move the filled pallet from the table to another location on the floor. The linear axis assists the KUKA robot in moving from the table to the second position on the floor.
- Stacker cane
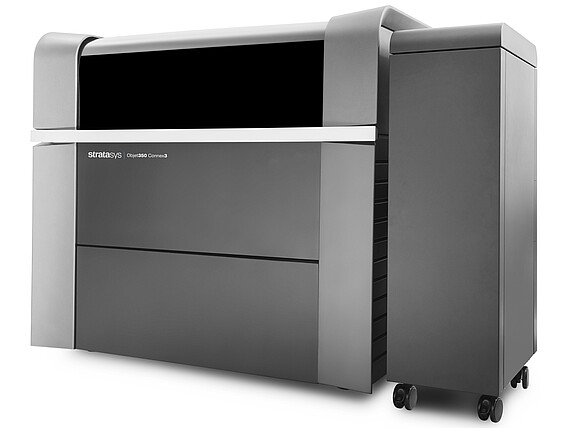
Rapid Prototyping System
An Object350 Connex3 Polyjet 3D printer is avaialble in the imes NIFE Lab.
Specification
- Resolution: x-axis: 600 dpi; y-axis: 600 dpi; z-axis: 1.600 dpi
- Layer thickness up to 16 µm
- Building space: 340 × 340 × 200 mm
- 8 print heads
- different material properties in one printing process
- Materials for the medical sector available



Identification & Control
Test Vehicles and Measurement Equipment
In order to test and to record data, the Institute of Mechatronic Systems has its own test vehicles.
Specification
- Vehicle Type: Volkswagen Golf GTE Plug-In Hybrid petrol
- Engine:1,4 l, 110 kW, 250 Nm
- electric engine: synchronous motor, 75 kW
- Drive: Parallel-Hybrid



Specification
- Vehicle Type: Volkswagen Touran diesel
- Engine: 1,9 l, 77 kW
- Drive: Front-wheel drive, manual transmission



Specification
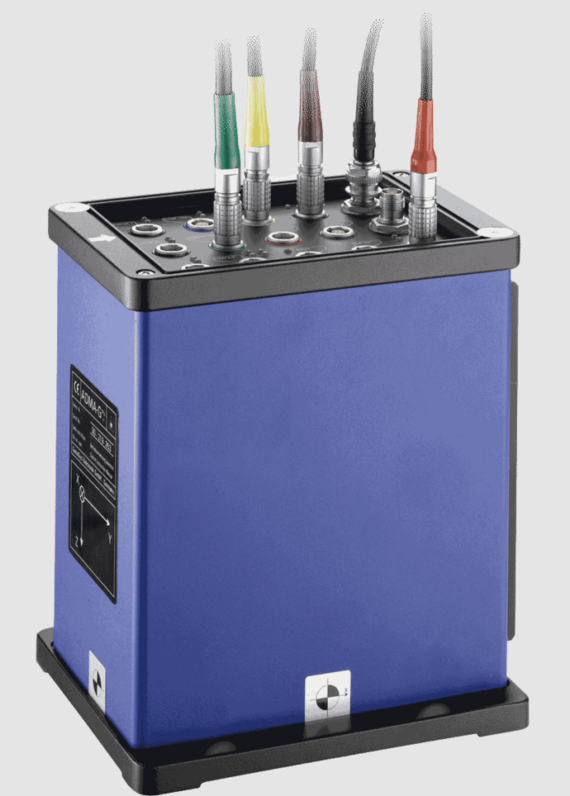
- Inertial measurement unit for vehicle dynamic measurements ADMA ECO+, GeneSys
- GPS- and Kalman Filter-based measurements
- measurements of accelerations and rotations
- funded by BMWi

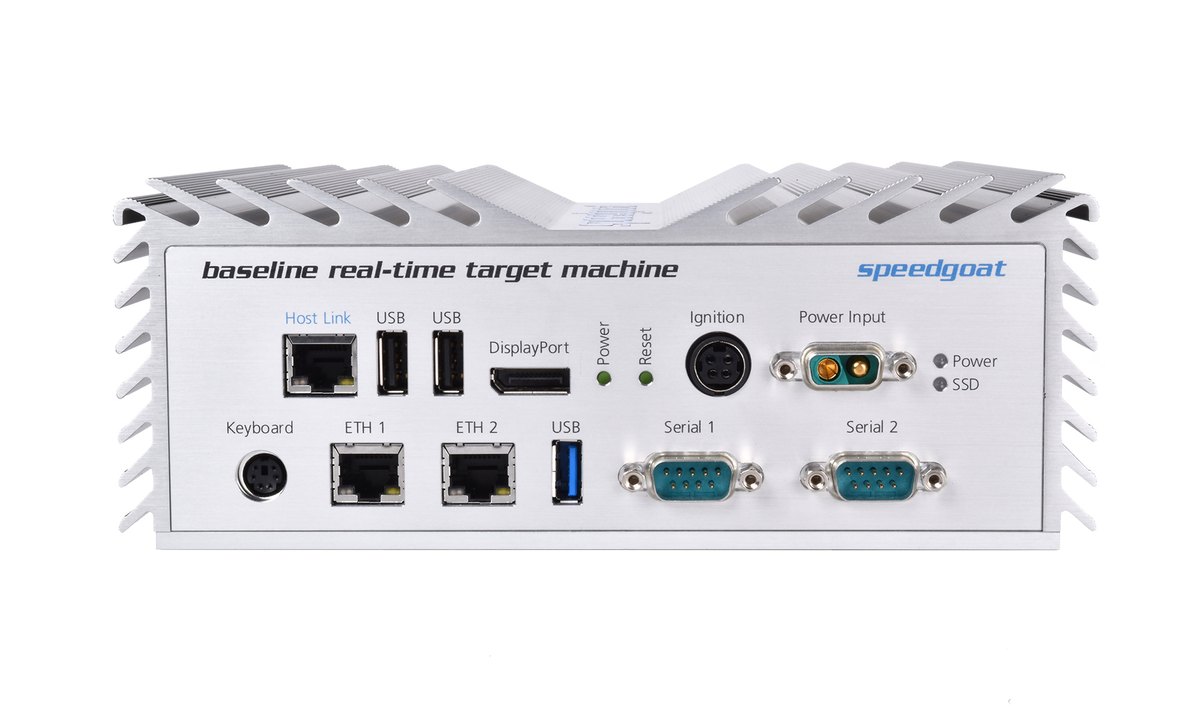
Specification
- Speedgoat Baseline Target-PC
- Real-time applications of Simulink models
- CAN-bus interface



Specification
- Dewesoft Data Aquisition System (DAQ)
- Recording von vehicle data in real-time
- Analog inputs
- CAN-bus inputs



Specification
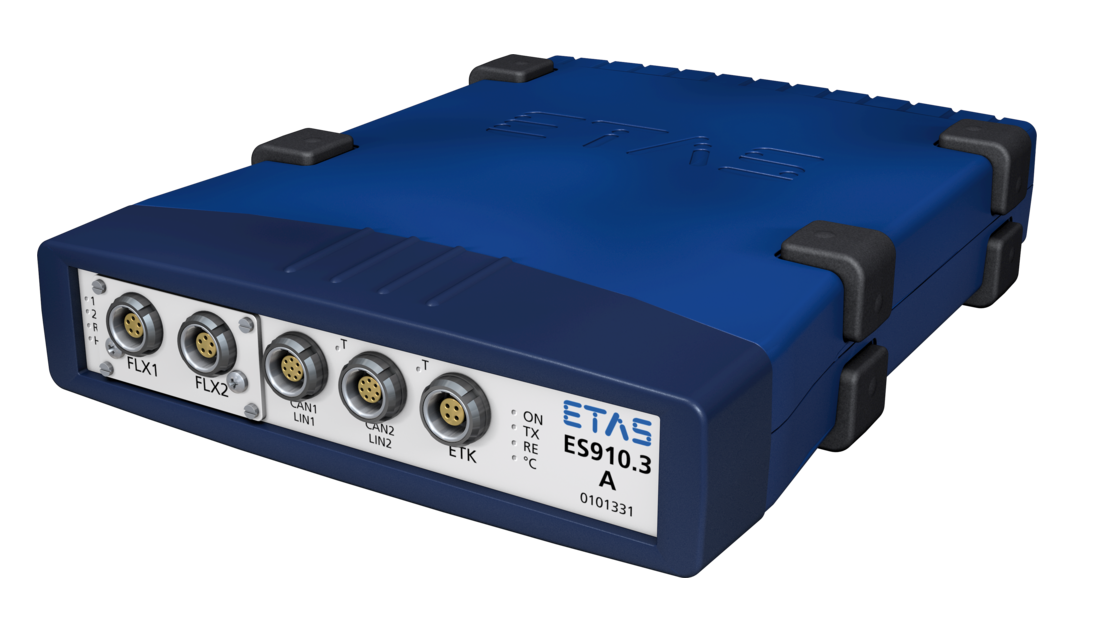
- ETAS ES 910 Target-PC
- Real time applications in vehicle
- CAN-bus interface



Medical Technology & Image Processing
Specification
- Voxel size: 0.1 - 0.3 mm
- Scan volume 14x14x24 cm³


Autoklav
To investigate the feasability to sterilize medical instruments we use the autoclave system Melag Vacuklav 23b+. It is a sterilization system class B, which is suitable for continuous steam vacuum sterilization processes.
Specification
- Stand-alone (no fixed water connection)
- Volume: 22 Liter
- Tray Dimensions: 19 x 42 x 2 cm (B x T x H)
- 230 V / 2500 W
- Weight: 48 kg
- Loading: 5 kg instruments



Optical Coherence Tomography
The Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is one of the most powerful emerging optical imaging modalities. The Swept Source Fourier Domain OCT of Thorlabs Inc. has the capability of producing high resolution, three dimensional image data.
Specification
- Center Wavelength: 1325 nm
- Spectral Bandwidth: >100 nm
- Imaging Volume: 10 mm x 10 mm x 3 mm
- Axial Resolution: ca. 10 µm
- Transverse Resolution: ca. 15 µm



Optical Navigation Systems
The Institute of Mechatronic Systems has optical navigation systems, that allow for 6DOF pose-calculations of objects in space. The laboratories are equipped with the following devices: NDI Polaris, Qualisys Oqus 4 and Advanced Realtime Tracking GmbH ARTTrack2.
Specification NDI Polaris und ARTTrack2
- Measuring accuracy: 0.3 mm
- Refresh-rate: 60 Hz
- Measuring range: Distances up to 4 meters



Specification Qualisys Oqus 4
Measuring accuracy: 0,1mm
- Refresh-rate: 480Hz (up to10 kHz with reduced FOV)
- Measuring range: Distances up to 25 meters



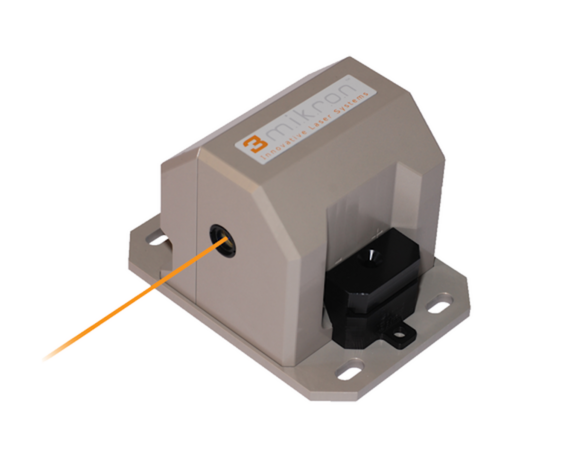
High Frequency Er:YAG Laser Source
The diode-pumped laser source DPM-15 (Pantec Engineering/3m.i.k.r.o.n) is well suited for ablating hydrous material due to its specific wavelength. Biological hard tissue (bone) as well as soft tissue can be processed with optical scanners in a volume of 10 x 10 x 10 mm3 and with tunable speed or ablation rate.
Specification
- Power output up to 9 W
- Pulse frequency 50 Hz to 500 Hz
- Focal diameter 400 µm
- Ablation volume 10 x 10 x 10 mm3 (extendable)



Mobile Coordinate Measuring Machine
The Institute of Mechatronic Systems has a mobile coordinate measuring machine (Faro GagePlus).
Specification
- Volumetric accuracy: 0,025 mm
- Spherical workspace having a diameter of 1,2 m



OP Microscope
Research is performed with a stereo operating microscope Allegra 50 from Möller-Wedel GmbH for scaled-up vision during clinically oriented application. Future image-guided interventions and further medical technogy development could profit from this device, e.g. in experimental ENT surgery.
Specification
- 5-step magnification changer (2x, 4x, 8x, 16x und 32x) at f=250 mm
- Coaxial halogen lamp illumination
- Stereo camera adapter



Robotics & Autonomous System
Hexa - Parallel Kinematic Machines
The Institute of Mechatronic Systems has several serial and parallel kinematic robotic systems. The laboratories are equipped with industrial articulated robots as well as a parallel 3(P)RRR planar robot.



Mobile Robot "KMR iiwa"
The KMR iiwa is a combination of a mobile platform (KMP 200 omniMove built in 2018) and a lightweight robot (LBR iiwa 14 R820). The robot can navigate autonomously and is designed for human-robot interaction. With its flexibility, the KMR iiwa is particularly suited for integration in an Industry 4.0 environment.
Specification
- Arm: 14 kg rated payload
- Arm: 820 mm max. reach
- Arm: 7 controlled axes
- Arm: Torque sensors in all joints
- Platform: 145 kg max. payload
- Platform: Obstacle detection with laser scanners and ultrasonic sensors
- Platform: 8 h battery operation time



Redundant Serial Light Weight Robot
Due to its integrated sensors and its redundant seventh axis the KUKA Light Weight Robot (LWR) is very well suited for human-machine-interaction. Its ligth weight of only 15 kg combined with a nominal load of 7 kg allows the robot to be energy efficient, flexible in its working position and to conduct a variety of assignments.
Specification
- 7 kg nominal load (max. 14 kg)
- 1.84 m3 workspace volume
- 0.05 mm repeatability
- 7 actuated rotational axes



Parallel Precision Robot
The H-824 6-axis-positioning system of Physik Instrumente (PI) GmbH & Co. KG is particularly suitable for high precision applications. In comparison with serial robots, this compact parallel robot with six degrees of freedom has a higher stiffness and reliability.
Specification
- 10 kg nominal load
- Travel ranges up to 45 mm / 25°
- 7 nm resolution
- 0.1 µm repeatability